VMware vSphere is a bundling Virtualization Package from Microsoft with the main component is EXSi and vCenter.
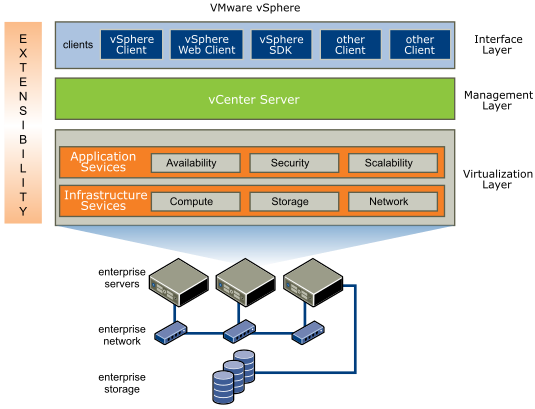
Interface layerAccess Management Management LayerVMware vCenter Server. Virtualization Layer Providing Infrastructure and Application Service (compute/storage/networking and availability/security/scalability).
Features and Components from VMware vSphere
- VMware ESXi : Virtualization Host.
- VMware vCenter Server : Centralized cluster management for EXSi Host.
- VMware vSphere Client : EXSi/vCenter Server Remote Client for windows PC.
- VMware vSphere Web Client : EXSi/vCenter Server Remote Client from a variety of Web browsers and operating systems.
- VMware vSphere SDKs : Features for third party solutions (API).
- vSphere Virtual Machine File System (VMFS) : A high performance cluster file system for ESXi virtual machines.
- vSphere Virtual SMP : Enables a single virtual machine to use multiple physical processors simultaneously.
- vSphere vMotion : Enables the migration of powered-on virtual machines from one physical server to another with zero down time, continuous service availability, and complete transaction integrity. Migration with vMotion cannot be used to move virtual machines from one datacenter to another.
- vSphere Storage vMotion : Enables the migration of virtual machine files from one datastore to another without service interruption. You can place the virtual machine and all its disks in a single location, or select separate locations for the virtual machine configuration file and each virtual disk. The virtual machine remains on the same host during Storage vMotion. Migration with Storage vMotion lets you move the virtual disks or configuration file of a virtual machine to a new datastore while the virtual machine is running. Migration with Storage vMotion enables you to move a virtual machine's storage without any interruption in the availability of the virtual machine.
- vSphere High Availability (HA) : A feature that provides high availability for virtual machines. If a server fails, affected virtual machines are restarted on other available servers that have spare capacity.
- vSphere Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) : Allocates and balances computing capacity dynamically across collections of hardware resources for virtual machines. This feature includes distributed power management (DPM) capabilities that enable a datacenter to significantly reduce its power consumption.
- vSphere Storage DRS : Allocates and balances storage capacity and I/O dynamically across collections of datastores. This feature includes management capabilities that minimize the risk of running out of space and the risk of I/O bottlenecks slowing the performance of virtual machines.
- vSphere Fault Tolerance : Provides continuous availability by protecting a virtual machine with a copy. When this feature is enabled for a virtual machine, a secondary copy of the original, or primary, virtual machine is created. All actions completed on the primary virtual machine are also applied to the secondary virtual machine. If the primary virtual machine becomes unavailable, the secondary machine becomes immediately active.
- vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS) : A virtual switch that can span multiple ESXi hosts, enabling significant reduction of on-going network maintenance activities and increasing network capacity. This increased efficiency enables virtual machines to maintain consistent network configuration as they migrate across multiple hosts.
- Host Profiles : A feature that simplifies host configuration management through user-defined configuration policies. The host profile policies capture the blueprint of a known, validated host configuration and use this configuration to configure networking, storage, security, and other settings across multiple hosts. The host profile policies also monitor compliance to standard host configuration settings across the datacenter. Host profiles reduce the manual steps that are involved in configuring a host and can help maintain consistency and correctness across the datacenter. Host profiles are also a component of vSphere Auto Deploy. The concept of an autodeployed host means that vCenter Server owns the entire host configuration and it is captured within a host profile. Certain policies require user input to provide host-specific values. To support Auto Deploy for host profiles, an answer file is created that contains the definitions for those policies.
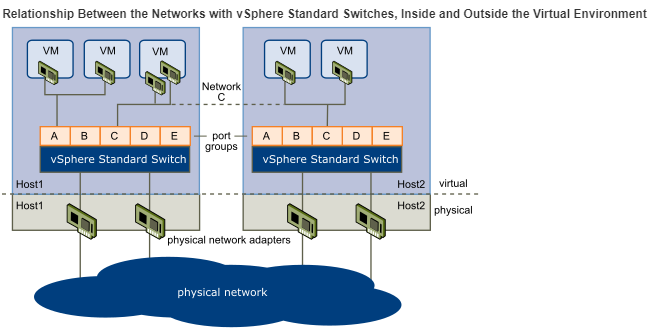
VMware vSphere Networking Architecture VMware vSphere has a set of virtual networking elements that lets you network the virtual machines in the datacenter like physical machines are networked in a physical environment. The virtual environment provides networking elements similar to those in the physical environment. They are virtual network interface cards (virtual NICs), vSphere Distributed Switches (VDS), distributed port groups, vSphere Standard Switches (VSS), and port groups.
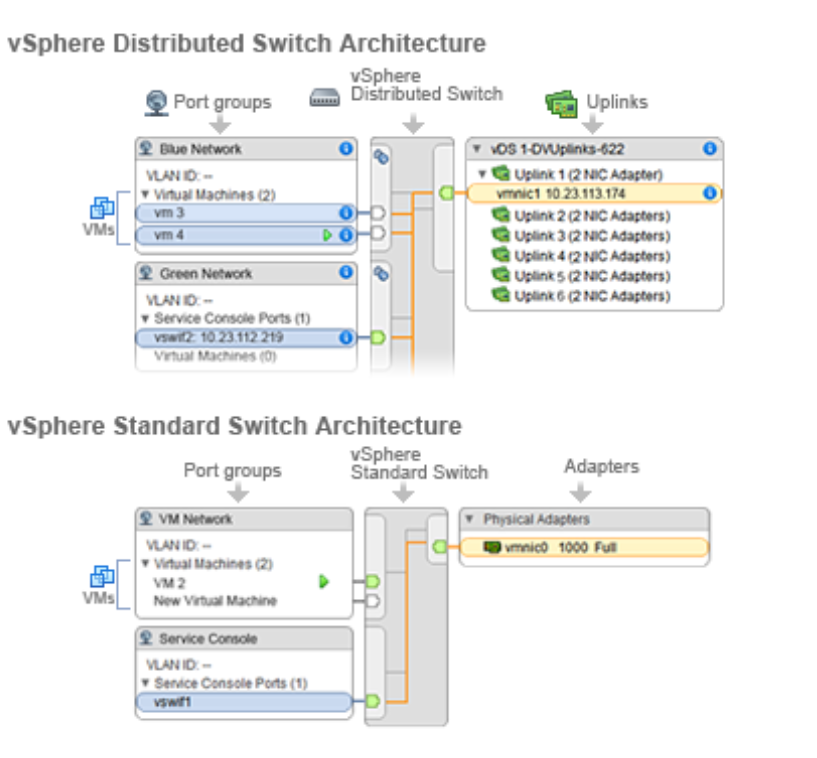
Networking with vSphere Distributed Switches
A vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS) functions as a single virtual switch across all associated hosts. This ability allows virtual machines to maintain consistent network configuration as they migrate across multiple hosts. Each VDS is a network hub that virtual machines can use. A VDS can route traffic internally between virtual machines or link to an external network by connecting to physical Ethernet adapters. Each VDS can also have one or more distributed port groups assigned to it. Distributed port groups aggregate multiple ports under a common configuration and provide a stable anchor point for virtual machines connecting to labeled networks.
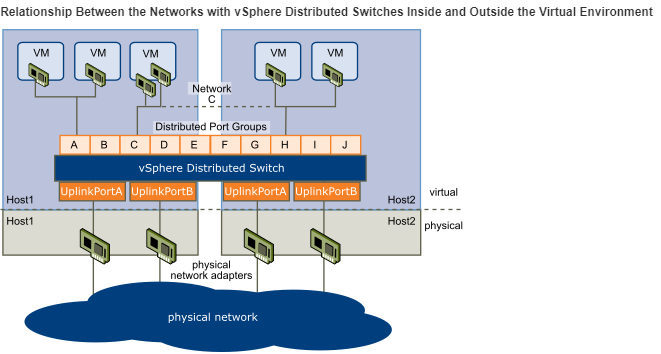
Networking with vSphere Standard Switches
With vSphere Standard Switches, each server has its own virtual switch: VSSs handle network traffic at the host level in a vSphere environment. A VSS can route traffic internally between virtual machines and link to external networks.
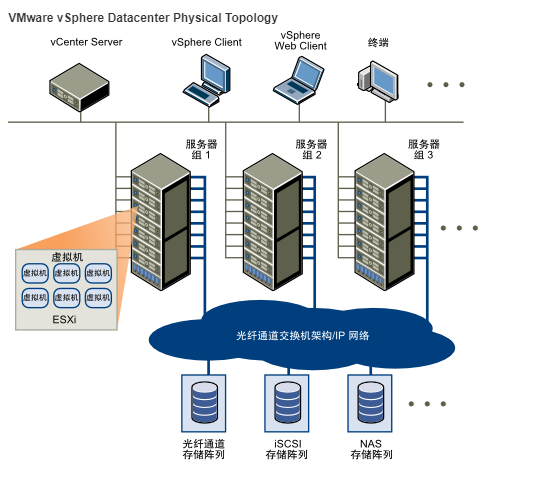
Storage Architecture
A datastore is like a storage appliance that delivers storage space for virtual machines across multiple physical hosts. Multiple datastores can be aggregated into a single logical, load-balanced pool called a datastore cluster.
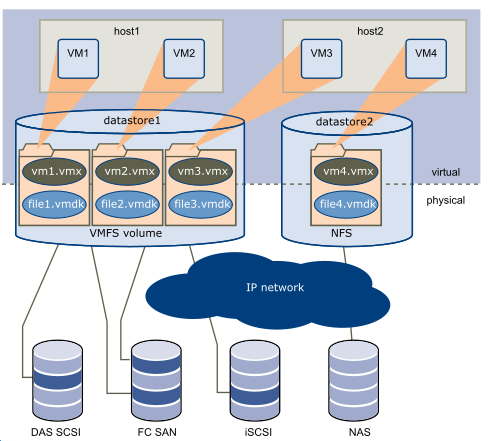
Datastores are virtual representations of combinations of underlying physical storage resources in the datacenter. These physical storage resources can come from the following sources: Local SCSI/SAS, or SATA disks of the server/Fibre Channel SAN disk arrays/iSCSI SAN disk arrays/Network Attached Storage (NAS) arrays.
VMware stores virtual machines as a package that includes the virtual machine settings file (filename.vmx) and the virtual disks (filename.vmdk). Each virtual machine is stored as a set of files in a directory in the datastore. The disk storage associated with each virtual guest is a set of files within the guest's directory. You can operate on the guest disk storage as an ordinary file. The disk storage can be copied, moved, or backed up. New virtual disks can be added to a virtual machine without powering it down. In that case, a virtual disk file (.vmdk) is created in VMFS to provide new storage for the added virtual disk or an existing virtual disk file is associated with a virtual machine.
VMware vSphere Networking Glosarium
For further reference : VMware vSphere 5.0 documentation VMware vSphere 6.x documentation