Disclaimer
A snapshot preserves the state and data of a virtual machine at a specific point in time. Snapshots provide a change log for the virtual disk and are used to restore a VM to a particular point in time when a failure or system error occurs.
- The state includes the virtual machine’s power state (for example, powered-on, powered-off, suspended).
- The data includes all of the files that make up the virtual machine. This includes disks, memory, and other devices, such as virtual network interface cards.
When you take a snapshot, you capture the state of the virtual machine settings and the virtual disk. If you are taking a memory snapshot, you also capture the memory state of the virtual machine. These states are saved to files that reside with the virtual machine's base files.
Any data that was writable on a VM becomes read-only when the snapshot is taken. VMware administrators can take multiple snapshots of a VM to create multiple possible point-in-time restore points. When a VM reverts to a snapshot, current disk and memory states are deleted and the snapshot becomes the new parent snapshot for that VM. A virtual machine provides several operations for managing snapshots such as creating, revert to any snapshot in the chain, and remove snapshots.
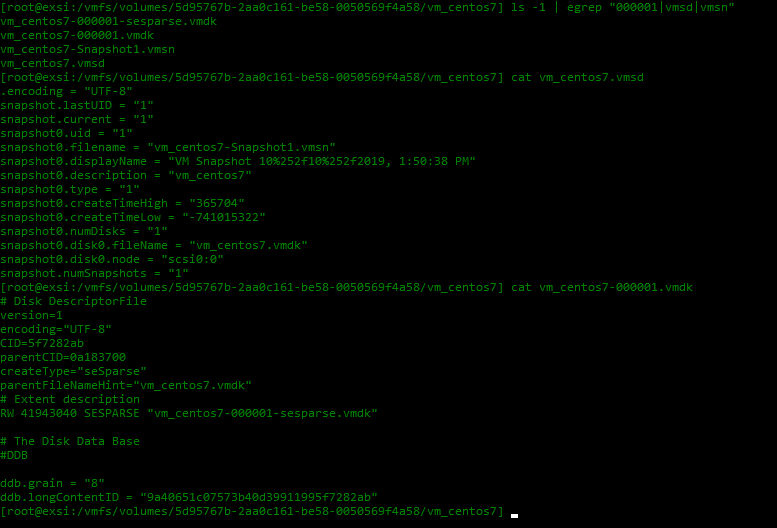
Snapshot Files
- .vmdk and --delta.vmdk
- .vmsd is a database of the virtual machine's snapshot information and the primary source of information for the Snapshot Manager.
- .vmsn the .vmsn file includes the current configuration and optionally the active state of the virtual machine. Capturing the memory state of the virtual machine lets you revert to a turned on virtual machine state. With nonmemory snapshots, you can only revert to a turned off virtual machine state. Memory snapshots take longer to create than nonmemory snapshots.
Usefull Notes
- In ESXi 5.x and later, snapshots descriptor and delta VMDK files will be stored in the same location as the virtual disks (which can be in a different directory to the working directory).
- Consolidate: Merges the hierarchy of redo logs. This is available in vSphere 5.0 and later.
- Reverting virtual machines to a snapshot causes all settings configured in the guest operating system since that snapshot to be reverted. The configuration which is reverted includes, but is not limited to, previous IP addresses, DNS names, UUIDs, guest OS patch versions, etc