CI/CD
CI : Continous Integration (test and building the artifact) CD : Continous Deployment (deployment)
"bagaimana proses pembuatan artifact (build code), testing, dan deployment ke server dilakukan secara otomatis"
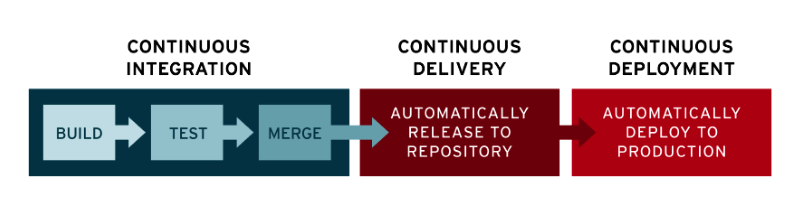
Continous Integration
- Keyword: verification by unit test, automated build process.
- Only building artifact.
- Its a culture. Its a practice in a software development.
- All team member trying to integrate their work frequently (daily)
- Each integration is verified by an automated build (including test) to detect integration errors
- Software Development Lifecycle:
- Plan -> Code -> Build (artifact) -> Test
- Release -> Deploy -> Operate -> Monitor
- Common mistake in CI
- Not putting everything into the code repository
- Not automating the build process
- Not triggering quick tests on every change
- Not fixing broken builds right away
- Typical CI
- Repository -> Build (install, download, test, build) -> push to the registry (need credential)
Continous Deployment
- Software release process
- Uses automated testing to validate if changes to a codebase are correct and stable
- Keywoard: package creation by CI process, script to configure the environment, deploy the packages.
- Authentication -> Image/Artifact Pull -> Ask for continue? -> Deployment to the server
GITLAB CICD WORKFLOW
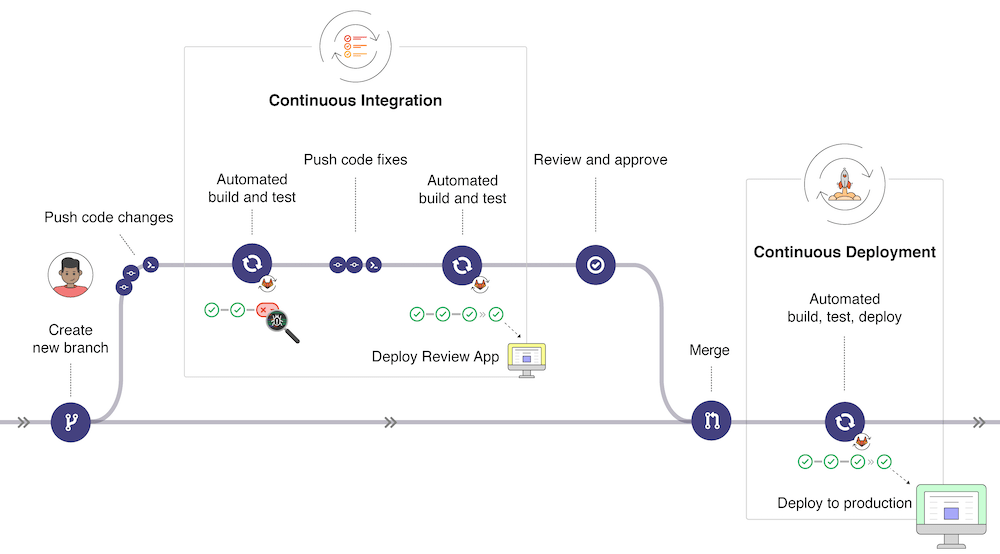
Gitlab Components
- Gitlab Server
- Gitlab Runner
Gitlab CICD Concepts
- Pipeline. Contains:
- Jobs : which define what to do. Executed by runners.
- Stages : which define when to run the jobs.
- Typical pipeline might consist four stages (build,test,staging,production)
- Methods : basic, directed acyclic graph, child/parent pipelines.
BASIC
.gitlab-ci.yml #must-exist-in-top-level-folder
stages:
- build
- test
- deploy
image: alpine
build:
stage: build
script:
- echo "This job builds something."
test:
stage: test
script:
- echo "This job tests something. It will only run when all jobs in the"
- echo "build stage are complete."
deploy:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "This job deploys something. It will only run when all jobs in the"
- echo "test stage complete."DAG
.gitlab-ci.yml #must-exist-in-top-level-folder
stages:
- build
- test
- deploy
image: alpine
build:
stage: build
script:
- echo "This job builds something quickly."
test:
stage: test
needs: [build]
script:
- echo "This test job will start as soon as build_a finishes."
- echo "It will not wait for build_b, or other jobs in the build stage, to finish."
deploy:
stage: deploy
needs: [test_a]
script:
- echo "Since build_a and test_a run quickly, this deploy job can run much earlier."
- echo "It does not need to wait for build_b or test_b."-
Jobs
- Pipeline configuration begins with jobs. Jobs are the most fundamental element of a .gitlab-ci.yml file
- Must contain at least the script clause.
-
Variables
- With Env Var you can control the behavior of jobs and pipelines.
- Store values you want to re-use
- Avoid hard-coding values in your .gitlab-ci.yml file.
- You can use it in .gitlab-ci.yml file, or project/group/instance variables